OPUS10 – More than Spare Parts Optimization
To many, OPUS10 – one of the software tools in Opus Suite – is synonymous with cost effective spare parts optimization. With its realistic modeling of technology and support solution, rapid calculations, and results that reduce the spare part investment by 30% or more – while also increasing system availability – OPUS10 has indeed become an industry standard in this field. But as you will find below, OPUS 10 also has much more to offer.
Spare Parts Optimization Software Built for Operational Readiness
Opus10 is the leading spare parts optimization software trusted by defense, aerospace, and asset-intensive industries. It helps you model, simulate, and optimize multiechelon spare parts networks, ensuring availability while minimizing cost. Whether you're planning sustainment strategies or managing complex supply chains, Opus10 delivers data-driven recommendations aligned with your performance goals.
OPUS10 is ideal for finding the most cost-effective answer to questions such as:
- What spare parts assortment should I have in stock, and how should I allocate it to different stock facilities to ensure maximum overall performance at the lowest possible cost?
- A high average performance is great but not enough. I have multiple performance requirements that differ per location and system type. What is the most cost-effective spare parts assortment and allocation for this situation?
- How should the spare parts solution be progressively adjusted to ensure cost-effective support during a time phased scenario (like a stepwise roll-out or phase-out of systems)?
- For each component and type of failure, should the component be repaired or discarded when it fails?
- Where is it optimal that repairs occur, locally or centrally?
- What will the spare parts inventory cost, given my target performance and support solution restrictions (if such restrictions apply)?
- How will efficiency and costs be affected, for example prices, failure rates or lead times increase by X%?
Evaluation of Support Solutions
While spare parts optimization is a core capability of OPUS10, and most common application, OPUS10 also provides indispensable decision support in a wide range of situations. It is possible to optimize the entire maintenance concept, to evaluate and compare alternative support solutions, and to make decisions regarding:
- What is the most cost-effective support organization structure?
- Where in the organization should maintenance equipment and personnel be located?
- Should all or part of the maintenance be outsourced?
- How many warehouses do I need, and where should they be located?
- What is the most cost-effective transport solution?
- How sensitive is my solution to changes or data inaccuracy?
- How should the support organization and spare parts inventory be adjusted during stepwise ramp up or phase-out?
Evaluation of Technical Systems
Another area where OPUS10 is applicable is evaluating different technical systems and finding answers to questions such as:
- What system design and configuration are optimal from a supportability perspective?
- Which component choice is the most cost effective from a life cycle perspective, the one with a higher price and better reliability, or the one with a lower price and somewhat lesser quality?
- What component upgrades and design changes are worth the investment due to increased performance and/or reduced cost of ownership?
Modeling and Optimization of Different Scenarios
OPUS10 is scalable and flexible, it can easily manage small-case scenarios with a handful of components and a few locations, while also catering to large programs with thousands of components and a complex support solution. Its effective optimization algorithms mean that even large cases will be optimized in seconds. OPUS10 is capable of accommodating;
- Repairable components and discardable / re-ordered items, as well as components that are sometimes repaired and other times discarded.
- Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance,
- Time phased scenarios where systems are gradually introduced or phased out
item specific support solutions, - Physical or maintenance based product breakdown structures
different criticality levels for components, - Multiple optimization requirements per e.g. location, unit or system type.
Read more about application areas
Related Resources
Case Study Spare Parts Optimization
Knowledge Center Spare Parts Optimization
Previous versions release information
Upcoming courses
| Course | Date | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Jan 13–15 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Jan 21–23 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| Opus Suite Introduction Course | Fev 25 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Mar 17–20 2026 | Grantham, UK | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Abr 14–16 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Abr 14–16 2026 | Stockholm, Sweden | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Abr 21–24 2026 | Bridgewater, UK | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Abr 22–24 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Mai 4–6 2026 | Stockholm, Sweden | Learn more |
| OPUS10 & SIMLOX Basic Course | Mai 4–8 2026 | Stockholm, Sweden | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Jun 23–26 2026 | Stamford, UK | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Jul 14–16 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Jul 21–23 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Ago 26 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Set 29–Out 2 2026 | Stamford, UK | Learn more |
| OPUS10 & SIMLOX Basic Course | Out 13–15 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Basic Course | Nov 3–6 2026 | Bridgewater, UK | Learn more |
| OPUS10 Extended Course | Nov 10–12 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
| OPUS10 & SIMLOX Basic Course | Dez 9–11 2026 | Virtual, North America | Learn more |
Quick tour
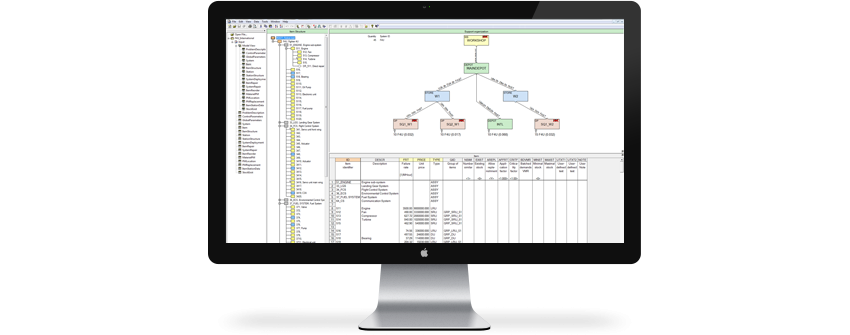
Data Input
The scenario to be analyzed is described in the OPUS10 model, which is based on tables that are used in a flexible way depending on, for example, complexity and desired level of detail. A “model view” gives the user overview and support when building the model, along with a graphic representation of the technical system and its product structure, as well as the logistic support solution.
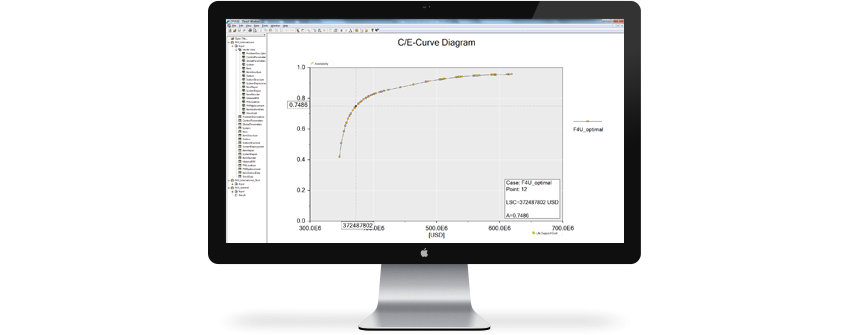
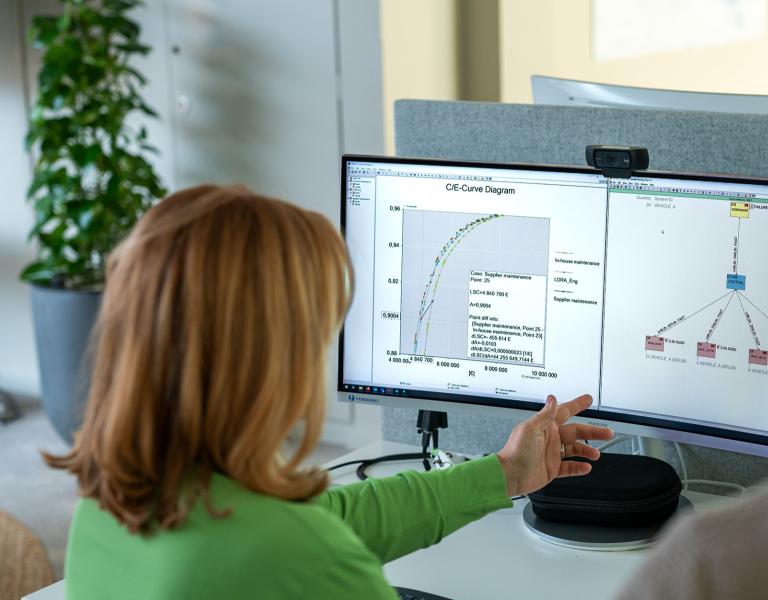
The C/E Curve
The Cost/Efficiency (C/E) Curve is a key step in OPUS10 optimization. A series of solution points is generated for a described scenario, showing maximum achievable system efficiency at different budgets. One solution point is selected, based on efficiency requirements and/or budget. The optimized solution behind the point can then be examined in the Table view, the Analysis view, or in the Reports section. By generating C/E curves for different scenarios in the same graph, their cost efficiency can be compared side by side.
Table View
The OPUS10 Results View features an interactive table allows you to easily select which solution points, parameters and dimensions to study. For instance, you can list stock levels, investments and service levels per component and location.
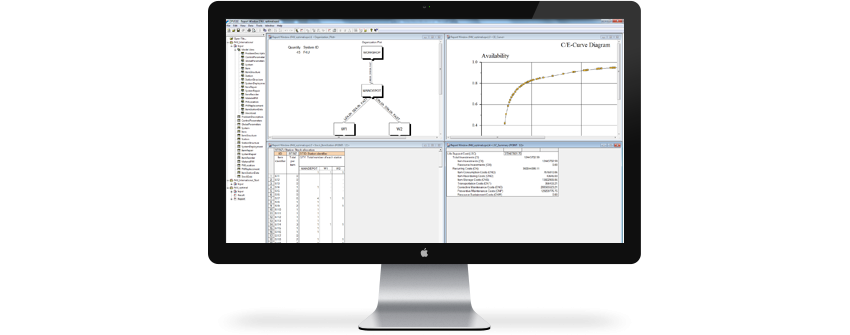
The Report Generator
The OPUS10 Report Generator provides reports that can be customized to show the results that are of interest. There is a great number of result tables and fields to choose from. The reports are easily exported to MS Excel or external databases and ERP systems.
Find out more about the decision support Opus Suite can provide to your organization.




